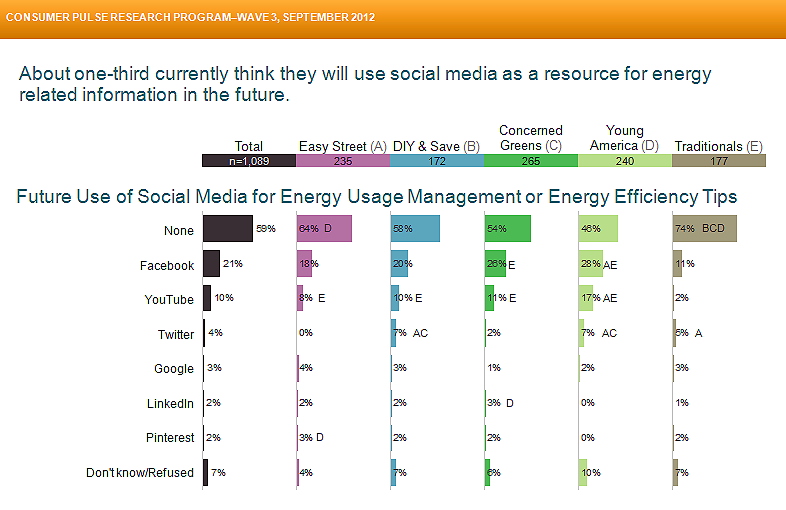
U.S. consumers are increasingly likely to visit social media sites to access energy information, according to the results of a nationwide telephone survey conducted recently on behalf of the Atlanta-based Smart Grid Consumer Collaborative (SGCC).
The Consumer Pulse Survey, Wave 3 documented frequent Internet— and, specifically social media— usage among 1,089 U.S. electricity consumers nationwide. The research was conducted between August 17 and September 5, 2012 by Michigan-based Market Strategies International.
About two-thirds of households contacted for the survey reported having both a high-speed Internet connection and a wireless network—offering excellent access to online account information and social media.
Technologically, these households are ready and able to adopt smart grid applications that leverage the installed infrastructure and their survey answers indicated that they probably also are willing. While relatively few respondents are using consumer information systems offered by their utilities just yet, a significant number of respondents said they would consider doing so in the future.
Out of the group of respondents to the Wave 3 survey, 19 percent said that a smart meter already had been installed in their homes. This number was low in comparison to actual current U.S. residential smart meter penetration, which exceeds 30 percent.
Among the top reasons that respondents cited for smart meter installation were: to save money (26 percent), to improve energy efficiency (18 percent), to reduce outages (11 percent), to reduce greenhouse gas emissions (10 percent), to help the environment (9 percent), and to obtain more accurate readings of meters and, therefore, more accurate billing (six percent).
The report also notes that consumer awareness of smart grid technology has remained relatively consistent over the past year—meaning that about half of the population still is unfamiliar with the term, “smart grid.” More explicitly, the analysts found that:
- Men know more about the smart grid (33 percent) than women (16 percent)
- Those in the affluent easy street demographic, on the whole, have less information than the do- it-yourselfers/savers and concerned greens—and surprisingly, traditionalists were the most informed (31 percent), while young Americans were the least savvy (15 percent)
- Respondents who live in the West and Midwest (30 percent and 26 percent, respectively) had more information on smart grids than respondents from the Northeast (20 percent) or South (22 percent)
"There continues to be a real need for consumer education around smart grid," said SGCC Executive Director Patty Durand. "The current low levels of public awareness on this issue represent both a challenge and an opportunity, but they must be acted upon."
Rising to meet that challenge, SGCC also revealed today that it plans to participate in the recently formed Department of Energy Smart Grid Customer Engagement Working Group which is managed by Philadelphia-based SmartEnergy IP, a strategy and research firm dedicated to smart grid customer education. Within the working group, the Smart Grid Consumer Collaborative will support the Stakeholders Relations Subcommittee—partnering with representatives from the energy and utilities industry to share information, build best practices and help to develop an engagement model for utilities rolling out smart grid programs.
"It is an honor to [be]… taking an active role within the DOE Smart Grid Customer Engagement Working Group. We look forward to promoting collaborative communication among stakeholders around increasing consumer awareness and engagement," added Durand.
Interestingly enough, while the study showed that consumers are likely to seek energy information online, SGCC’s own social media site does not draw a crowd. This reporter found that just 330 Facebook (News - Alert) users “like” the SGCC page—so perhaps the collaborative should add a few bells and whistles to boost its audience share.
Edited by
Jamie Epstein